In the search for business riches, the goldmine is data. Today, organizations always have more data to analyze, manipulate, and generate insights to power their growth aspirations. It forms the foundation of business intelligence by generating key insights and driving decision-making. But as we embrace tech advances, we face more significant risks. Hackers are always on the prowl, looking for gaps to sneak through and grab valuable data. This is where data security management steps in, throwing a protective arm around our vital information.
The risks, however, are all too real. A whopping 493 million ransomware attacks were reported globally last year—and it’s costing us more than ever, with the average data breach price tag hitting a steep 4.45 million USD in 2023. It’s a loud wake-up call, urging businesses to shield themselves with stronger data security to avoid financial hits and tarnished reputations.
In this post, we’ll provide easy-to-follow strategies to get data security management right, so you’re ready to fend off cyber attacks and keep your trust intact with those who matter—your stakeholders and customers.
What is Data Security Management?
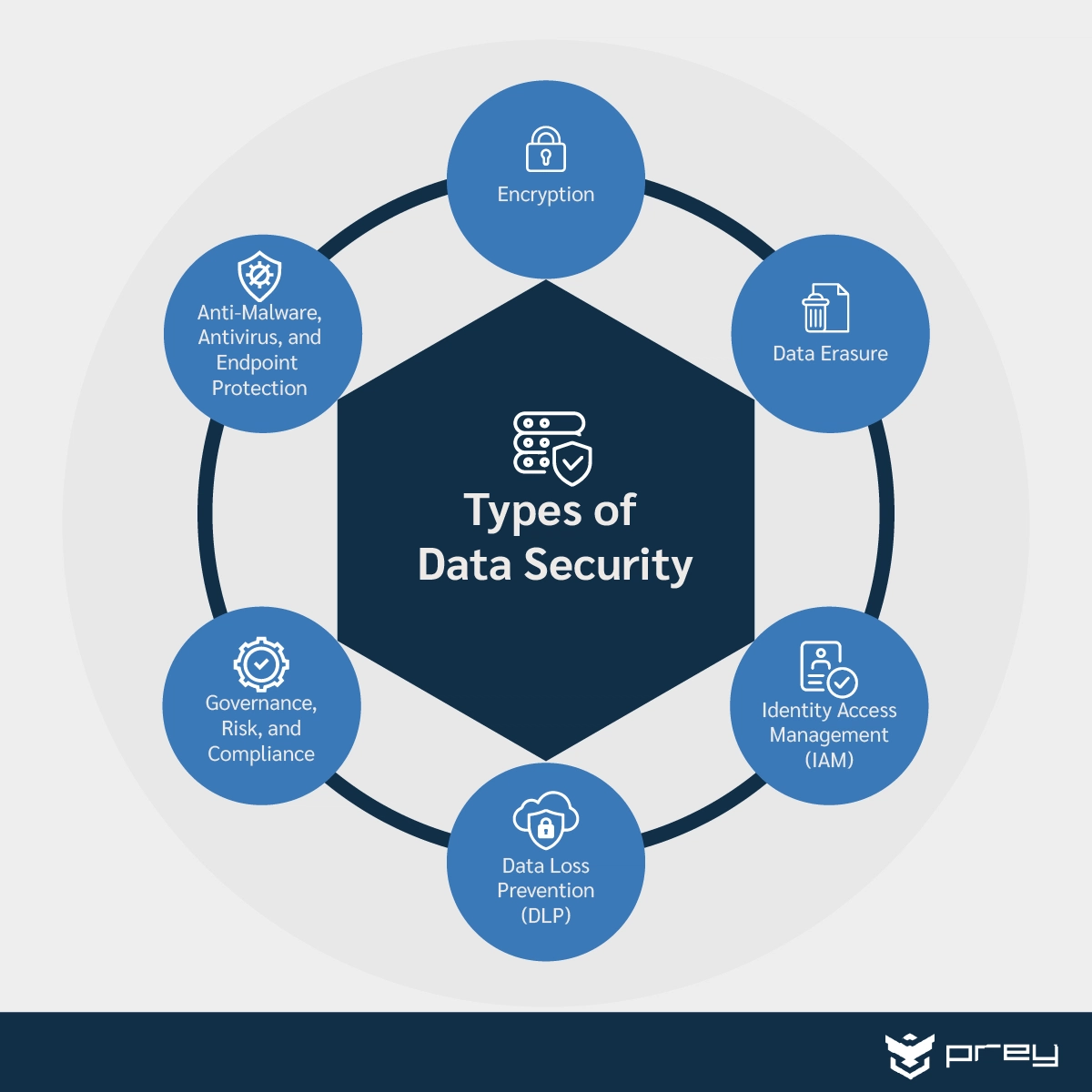
Data security management is the process of safeguarding sensitive business data from cyberattacks using multiple techniques, strategies, and practices. It’s a crucial preemptive measure that protects digital assets such as documents, files, images, and other intellectual property from cyber criminal activities.
A well-managed data security operation also considers the threat that insiders pose, including human error. It typically involves setting up and enforcing information security policies, monitoring IT systems for security risks and vulnerabilities, and implementing data security best practices across the enterprise.
Why is data security management so important?
In the current digital-first economy, every user submits sensitive and personally identifiable information (PII), including credit card details, to businesses. Although organizations are liable to keep this information guarded, they often fail. It leads to a loss of trust and business revenues.
Over the last few years, poor data security has impacted corporations, individuals, and governments. In 2022, more than 65% of companies in the US faced a cyber threat due to external factors. Globally, over 6 million data records were exposed through breaches in just the first quarter of 2023. Unfortunately, these records are sold off to other bad actors, who will potentially use them to launch a fresh wave of attacks like phishing and brute-force entry.
Data security impacts businesses financially, reputationally, and also regulatory. Compliance risks will only grow in the coming years as new data security regulations are enacted in the EU, Singapore, and other major economic zones. Many of these new rules will force companies to pay restitution to customers who lose data in a breach.
Benefits of Data Security Management
Securing business-critical data requires organizations to have absolute visibility into their system and implement measures like encryption, data masking, and automated audits. Robust data security management that evolves with the changing landscape of cyber threats is essential. It will help you:
- Reduce incidents of cyberattacks by proactively detecting threats and malicious intent and mitigating them before too much damage is done.
- Retain customers by ensuring that their data is secure.
- Stay compliant with data privacy laws and other governance regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act).
What types of data should be secured?
The first step of data security management is data discovery. It involves the identification of data sources and locations where data is stored. Data could be stored in servers, data centers, file shares, electronic devices (laptops, desktops, mobiles, portable drives), and cloud platforms. The sheer volume of data that organizations generate makes data security overwhelming.
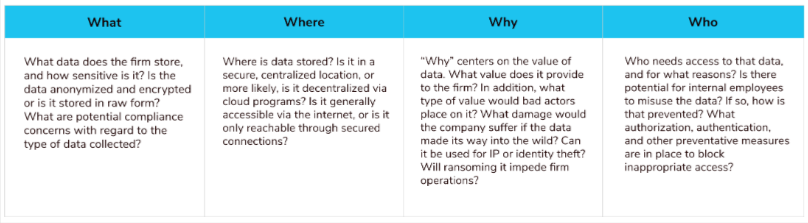
To kickstart robust data security management, establish a mechanism to continuously classify or tag data based on its significance to your business. Consider factors such as the data’s role in growth, your organization’s risk tolerance, and the potential repercussions on your organization if the data were to be compromised or exposed.
From a data security point-of-view, data is classified into three categories:
1. Restricted data with the highest level of security
The kind of data your organization uses, confidentiality agreements, and strict security guidelines fall under this category. If restricted data falls into the hands of bad actors, there will be irreparable damage.
Example: Customer information.
2. Private data requiring moderate security measures
If your organization possesses data that they may not want to share with the world but is also not a secret, it can be categorized as private data.
Example: Business financials.
3. Public data that is not a security priority
Any data that is not likely to be a security or reputation threat can be categorized as public data. It constitutes data that is available in the public domain.
Example: Marketing brochures.
While these are the broad data classifications, you can further bucket the data. Most organizations index data by evaluating its level of sensitivity. The key is to focus on the most critical data and ensure it’s secured.
The Key Threats to Data Security
Cyber attackers employ diverse tactics to breach systems. Despite advancements in cloud and AI/ML technologies, cybercriminals remain a step ahead, using equally advanced methods. Combatting these threats effectively hinges on a solid data security strategy grounded in a thorough understanding of the risks involved. The threats to data security include:
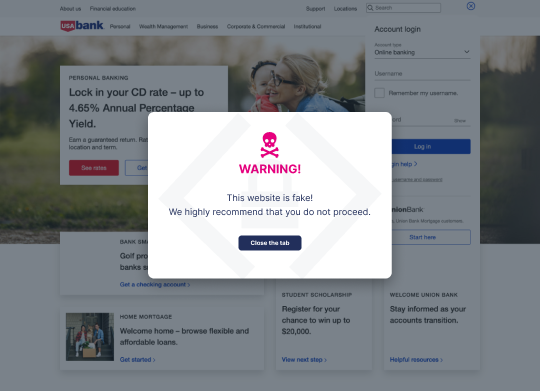
Website Spoofing
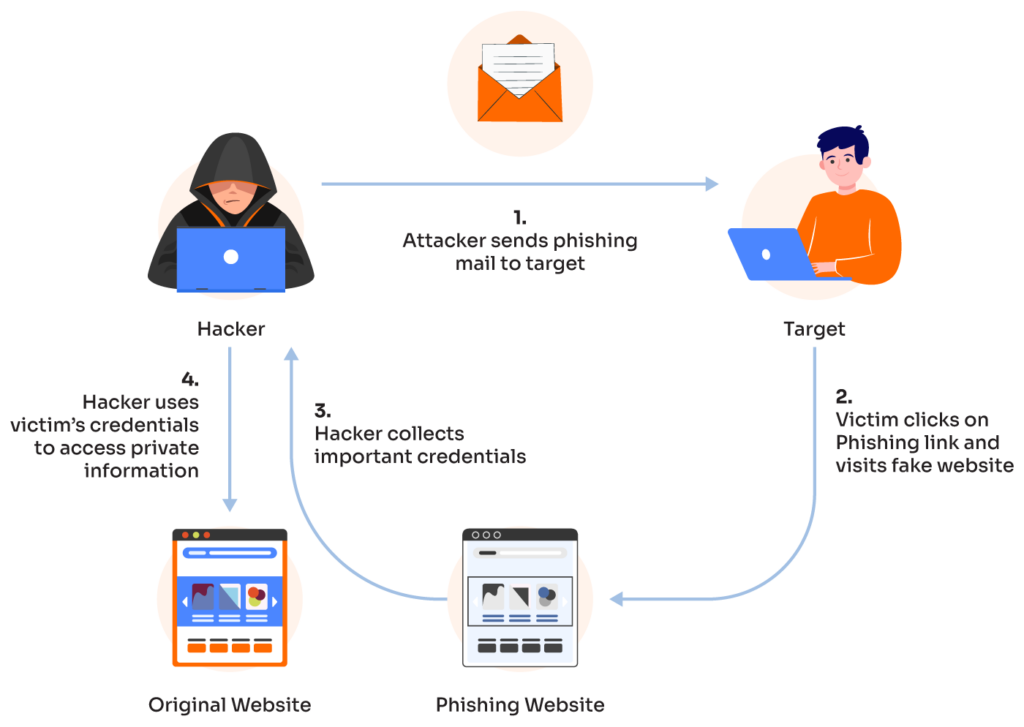
Website spoofing is the act of creating a fraudulent website that mirrors a trustworthy, well-known site. The fake site might feature similar URLs, logos, layouts, and content, making it difficult for users to distinguish it from the real one. Cybercriminals often use phishing emails or manipulate search engine results to lure victims to these spoofed websites.
Malware
Malware and ransomware, along with worms and trojans, represent a formidable spectrum of malicious programs designed to disrupt your regular business activities or exfiltrate sensitive data. These threats are expertly crafted to infiltrate your systems, posing a constant and evolving threat to data security.
Emails with Phishing Links
One of the most prevalent cyber threats people succumb to is phishing scams. These schemes typically involve sending potential victims an email that seems to be from a trustworthy source, such as the IRS. These messages often create a sense of urgency, encouraging you to click on a link that directs you to a malicious website seeking to harvest your personal information.
Popular phishing scams include:
- Deceptive Phishing: The most common type, where attackers impersonate a legitimate company to steal people’s login credentials or personal information
- Brand Impersonation: Posing as reputable brands to lure you into providing personal data on fake—but authentic-looking—spoofed websites.
- Spear Phishing: Targets individuals with personalized emails based on gathered data about the recipient to make the scam more convincing.
- Smishing: Utilizes SMS texts to trick recipients into clicking malicious links or providing personal information directly via message.
Procuring Breached Data
Once hackers gain unauthorized access to confidential information through a successful cyberattack, they can sell the compromised data at a premium. This data, which often includes emails, usernames, and phone numbers, can be purchased by other attackers to infiltrate accounts further. This initiates a potentially relentless chain of attacks, perpetuating a cycle of data breaches and heightened security risks.
Malicious Employees or Human Error
When you give an employee high-trust privilege, you essentially transfer confidential data into their hands. If an employee with high-privilege access and credentials parts ways with the organization voluntarily or involuntarily, they might steal or harm business-critical data.
But more often than not, good employees simply make mistakes that could put an organization’s data security in jeopardy. It can range from improper credential management to engaging with malicious content.
11 Ways to Get Data Security Management Right
Ultimately, your data security is only as strong as your weakest link. A robust data security management strategy must cover all the bases and close security loopholes in operational and technical processes.
Enhance your data security posture by following these best practices:
1. Protect your website from spoofing with Memcyco
Providing real-time protection against website spoofing and brandjacking, Memcyco secures enterprises and their customers with our end-to-end solution. An active tracking sensor embedded in your company’s authentic website ensures immediate attack detection and alerts, in-depth forensics, and innovative mitigation measures, thereby safeguarding the critical time window of exposure between fake site creation and takedown.
2. Include compliance regulations
Include compliance regulations in your data security framework since they are built for that purpose. These compliance regulations mandate organizations to build strong defenses against threats and reduce risk.
3. Clear data security policy
Define and enforce your security policy at an organizational level. The policy should clarify how sensitive data must be handled and outline the consequences of mismanaging data.
4. Recovery and backup plans
Put a recovery plan in place and also include a backup strategy. You can set an automated workflow that begins with encryption, backup, and storage of critical business data in disruptive scenarios like breaches.
5. Limit personal devices
Avoid the use of personal devices, including laptops, for work. Instead, you can provide your employees with corporate devices that allow only secure and trusted access to your network. It will also help you in enforcing your security policy.
6. Train employees in cybersecurity awareness
Conduct regular training and awareness sessions to help your employees identify, flag, and avoid cyberattacks like ransomware, phishing, and password management practices.
7. Trust no one
Implement Zero Trust and least privilege policies so that you don’t give too much control over your data and IT infrastructure to an individual.
8. Build a data security team
Build a strong cybersecurity team that can handle your data security daily. Having a specialized data security team might seem like a stretch. However, it is a worthy investment in the context of cyber threats.
9. Leverage automation
Automate the data classification process based on the level of sensitivity so that you prioritize your data security management plans efficiently.
10. Regular access reviews
Review access controls and privileges at regular intervals. It will help you identify and terminate any redundant roles with unnecessary access to data.
11. Plug vulnerable gaps
Conduct regular vulnerability evaluation tests to detect and plug any security gaps that could be leveraged to gain illegal access to your system.
Manage Website Data Security in Real-time with Memcyco
Data security is undeniably a top priority in today’s fast-evolving tech landscape. However, as we forge ahead with technological advancements, cybercriminals are constantly finding new avenues to breach systems. In this precarious environment, organizations must proactively devise and enact robust data security management strategies to safeguard their operations and ensure the safety of their customers—and their data.
A vital component of a formidable data security management strategy is protecting your all-important business website from spoofing fraud using Memcyco. Its agentless solution issues real-time Red Alerts to users visiting fake sites, and provides organizations with complete visibility into the attack, allowing them to take remediating actions quickly.
Learn more about how Memcyco’s PoSA is helping organizations enhance data security when you book a demo today.