Brace for impact—CISOs and IT professionals are gearing up for what promises to be an intense year in cybersecurity. Cybercriminals are readying themselves with increasingly cunning tactics against unsuspecting organizations and users. From leveraging artificial intelligence in creating bespoke malware to launching impressively uncanny spoofed sites, the risks are becoming increasingly intricate and difficult to predict.
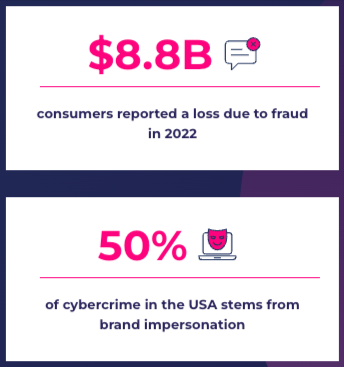
To grasp the magnitude of these threats, consider that the estimated cost of cyberattacks worldwide is rising, projected to reach over USD $20 billion by 2026.
Fortunately, there’s still time to prepare. That begins with understanding the shifting risk landscape, including insights into the types of cyberattacks expected in the coming year and how to defend against these threats.
2024 Cyber Attack Projections – Trends and Predictions
1. AI will empower fraudsters and amateur attackers
In 2023, AI went mainstream among legitimate users and cybercriminals alike. Its role in enabling and thwarting cyber threats is very much an emerging picture, but its impact is already felt as malefactors are embracing AI on several levels.
This year we’ll likely see more generative AI tools like BadGPT and EvilGPT, making it easier for attackers to find and exploit vulnerabilities programmatically with little to no cybercrime skills. AI/ML is also a catalyst for developing and selling sophisticated AI-powered spear phishing kits on the Dark Web, essentially using AI to bridge the cyber skill gap among online malefactors.
With these tools, fraudsters can spear phish more victims by automating the manual tasks entailed in researching the targets of attacks and crafting convincing email messages to trick them.
Another contribution of AI technologies to cyber attackers’ tactics is in their ability to generate emails, audio, images, and videos that are almost indistinguishable from the real thing (by now, you’ve probably heard of ‘deep fakes’). These capabilities enable malefactors to impersonate executives, spread misinformation, and sow social discord.
2. Supply chain attacks will grow in number and scale
Malefactors who want to victimize multiple targets in the enterprise world are choosing software and digital service supply chains as attack vectors. Cybersecurity Ventures forecasts that the yearly worldwide expense due to attacks on software supply chains will soar to an astounding $138 billion by 2031. This marks a significant increase from $60 billion in 2025 and $46 billion in 2023, reflecting an annual growth rate of 15 percent.
In 2023, the MOVEit hack affected millions of individuals and over a thousand businesses. We also saw breaches with SSO providers and even Facebook, exposing names exposing the names and email addresses of all the clients that used its customer support system.
As supply chains become more complex and include more moving parts, their attack surface grows to include more third-party components that fraudsters can compromise. Developers are increasingly targeted in supply chain attacks via software package managers and weaponized OSS libraries.
3. Businesses will be collateral damage of cyberwarfare and hacktivism
The geopolitical turmoil of 2023 led to a massive increase in state-sponsored attacks, hacktivism, and even false hacking claims that led to unnecessary cybersecurity investigations. Along with ongoing global conflicts, 2024 will have no fewer than 40 national elections worldwide, including in the UK and US presidential elections—and the 2024 Paris Olympics.
While cyberwarfare and hacktivism aren’t new, the commoditization of cybercrime makes it increasingly more complex to draw the lines between so-called commercial ransomware-as-a-service, malware-as-a-service, DDoS-as-a-service, and politically-driven attacks.
Hacktivism and cyberwarfare in 2024 are about spreading malware and disrupting operations as much as they are about spreading misinformation and destabilizing trust relationships in the digital realm. According to Gartner, by 2028, enterprise spending to battle misinformation will surpass USD $30 billion, cannibalizing 30% of cybersecurity and marketing budgets to fight in this AI-enhanced arena.
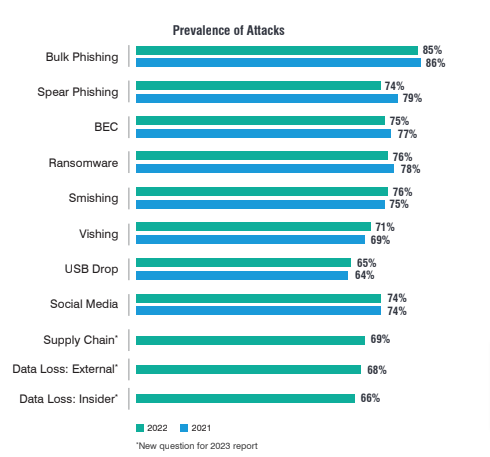
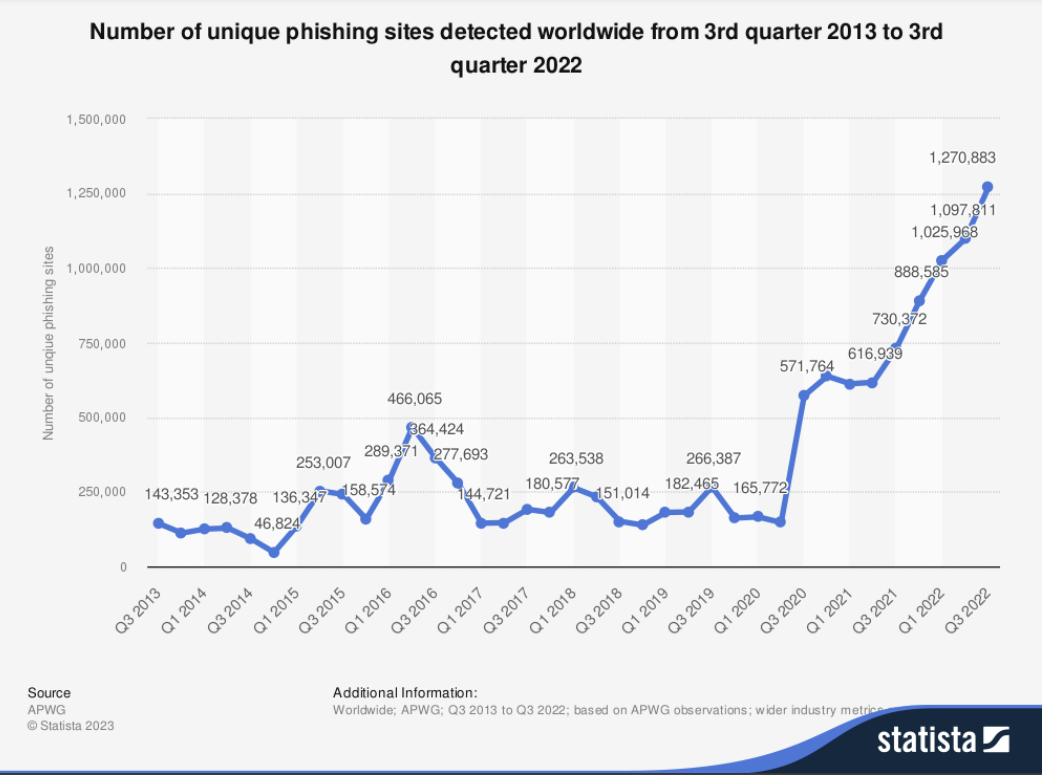
4. Cybercriminals will employ more alternatives to traditional phishing
Email phishing is a technique as old as online fraud, but its effectiveness may be dropping as email service providers, and system administrators employ sophisticated tools to filter out potentially harmful emails. So what are cyber crooks to do? The answer is ‘turn to creative means of executing digital fraud and send traffic to spoofed websites.’
With AI-powered voice chatbots, voice phishing (vishing) will continue to grow, and scammers will get better at monetizing our supposed trust in voice calls over online interactions.
Other channels that cybercriminals are embracing are QR codes, search engine malvertising, SEO poisoning, and social media platforms, where shortened links to malicious targets cannot be scanned or filtered.
5. MFA will no longer be enough to protect online identities
Secure management of online identities will continue to be a challenge for businesses in 2024, as organizations will be racing against threat actors, adapting their tactics in response to the increasing adoption of multi-factor authentication (MFA). Some organizations will be turning to passwordless access management to thwart the threat, but that might not cut it either.
According to CyberArk infosec researchers, session hijacking will account for 40% of all cyberattacks in 2023, with malefactors bypassing authentication mechanisms by exploiting third-party vulnerabilities and using stolen session tokens.
6. Malware and ransomware strategies will evolve
Ransomware actors had a good 2023, so in 2024, malware and ransomware are bound to continue disrupting business operations, costing organizations significant sums of money. Fraudsters will likely expand their portfolios, employing more zero-day vulnerabilities and polymorphic malware that learns and adapts between attacks.
Another interesting shift we may see this year is threat actors employing multi-pronged ransomware payloads, where victims are forced to continue paying over time to avoid a breach or loss of data. We might also see more ransomware threat actors reporting their victims to the SEC and other regulatory bodies. This seemingly bizarre tactic actually pressures organizations to pay up, in order to avoid public disclosure and potential regulatory consequences.

Corporate Strategies for Preempting Cyber Threats
To combat evolving cyber threats effectively in 2024, businesses must adopt dynamic and sophisticated defense strategies. This involves upgrading technology and nurturing a culture of cybersecurity awareness and preparedness.
Implementing Advanced Threat Detection Systems
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, legacy security systems may need to catch up. Organizations need to invest in more advanced threat detection systems capable of evolving with the threat landscape. These systems offer adaptability, real-time threat detection, predictive analyses, automated threat response, and comprehensive monitoring.
Strengthening Cyber Threat Intelligence
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) is essential to a robust cybersecurity strategy. Strengthening CTI involves developing a comprehensive framework to effectively understand, analyze, and act upon potential cyber threats.
This framework should include a variety of sources, such as industry reports, threat databases, and intelligence-sharing platforms. Businesses will need to collaborate with other organizations, cybersecurity experts, and government agencies to share threat intelligence, enhancing collective defense capabilities.
Enhancing Digital Trust
According to IBM, 81% of executives view security, assurance, and trust as brand differentiators. The same survey also found that 9 in 10 consumers say trust is the most important deciding factor when choosing a brand. However, trust is hard to earn and sustain when fraud is rampant and with malefactors adept at spoofing familiar and trusted brands.
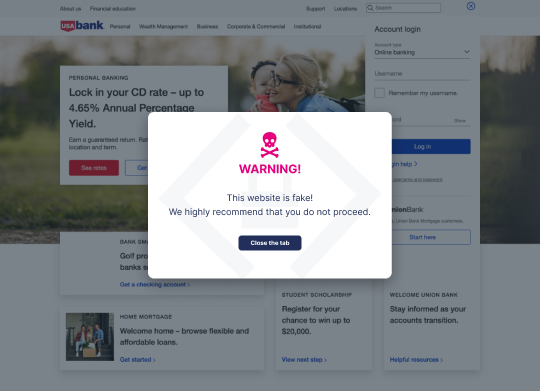
Digital trust depends heavily on the brand’s ability to detect, evaluate, and adequately respond to attacks, not only on the business and its infrastructure, but also on its clients, customers, and partners. Protecting your brand from impersonation attacks and ‘spoof-proofing’ your website requires a user-first approach to digital trust enablement and the right set of tools to facilitate it.
Keeping the Keys to Your Kingdom Safe From Website Impersonation Attacks
Memcyco’s solution offers an advantage over traditional website impersonation protection services and anti-phishing solutions by continually detecting impersonation-related attacks in real-time—protecting business, customers, employees and partners. It helps you stay ahead of fraudsters and protect your digital assets with brand impersonation monitoring, alerting, and protection.
Navigating the Cybersecurity Gauntlet of 2024
In 2024, organizations will face an onslaught of sophisticated cyber threats on all fronts. The coming year is shaping up to be a litmus test for cybersecurity defenses worldwide.
Passing that test with flying colors means pivoting from an ‘aftermath damage limitation’ footing to one of preemptive real-time detection and proactive attack obfuscation: the kind of capabilities innovators like Memcyco are bringing to market.
A cybersecurity storm may be coming, but the well-prepared organization will ride it out without fear—and enjoy a safe and prosperous 2024. Safeguard your business and your customers, with real-time defense with Memcyco. Book a demo