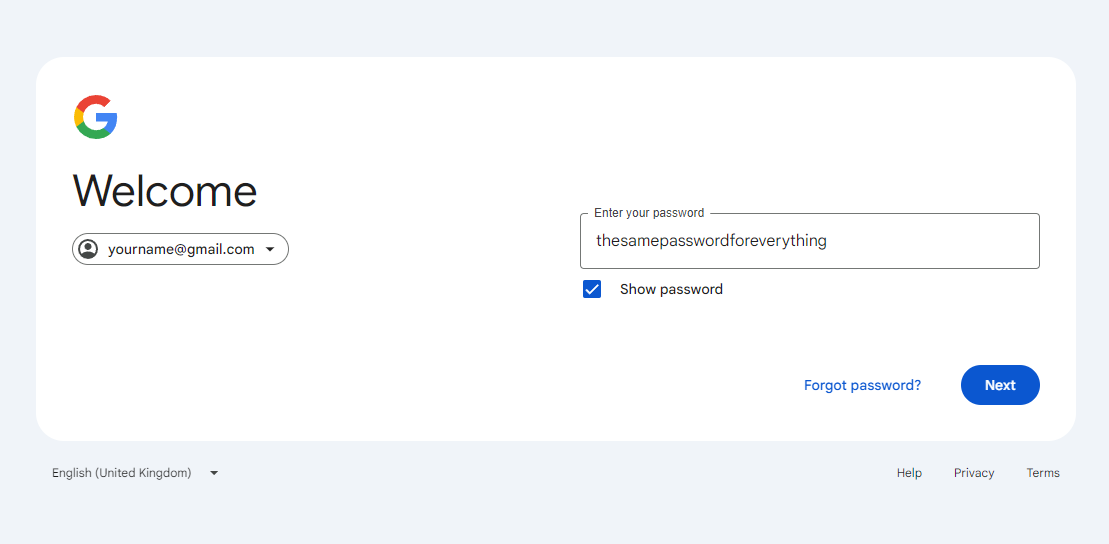
We’re in an era of connectivity and convenience, but this has also opened the floodgates to a new wave of cyber threats. Among the most insidious and pervasive is credential stuffing, a cyberattack that exploits the human tendency to reuse passwords across multiple online accounts.
This threat is more than just a digital inconvenience. Verizon’s 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report reveals that more than 49% of breaches caused by external actors involve stolen credentials.
But the fight against credential stuffing isn’t hopeless. By understanding the threat and implementing proactive security measures, we can significantly reduce our risk.
What is Credential Stuffing?
Credential stuffing is a cyberattack in which malicious actors leverage lists of stolen or leaked usernames and passwords to gain unauthorized access to user accounts across various online platforms. Cybercriminals often obtain these credentials from previous data breaches, phishing scams, or even website impersonation attacks, tricking unsuspecting individuals into unknowingly divulging their login information.
In many cases, this stolen data isn’t used immediately but is sold on the dark web, making it a persistent threat even after the initial compromise, particularly for financial institutions like banks. Implementing robust security measures and fraud protection policies is crucial to mitigating this risk.
Attackers employ automated tools like botnets and scripts to rapidly test these stolen credentials across various websites and services. The success of credential stuffing hinges on the unfortunate habit of password reuse, often facilitated by phishing attacks that lead unsuspecting users to malicious websites. Many individuals use the same or similar passwords across multiple accounts, making them vulnerable to this attack.
The threat of credential stuffing is on the rise due to:
- Data breaches and website impersonation: Creating a vast pool of compromised credentials readily available to attackers.
- Password reuse: Amplifying the impact of a single credential compromise.
- Automation: Making attacks highly efficient and difficult to detect.
- Dark web marketplaces: Providing easy access to stolen credentials for malicious actors.
Successful credential stuffing attacks can have severe consequences, ranging from account takeover and identity theft to ransomware attacks, financial fraud and reputational damage.

What is a Brute Force Attack?
A brute force attack is a type of credential stuffing attack in which cybercriminals use brute force to crack passwords or PINs. They systematically try every possible combination of characters until they find the correct one. This trial-and-error approach relies on sheer computing power and persistence rather than any specific vulnerability in the system, and it presents a challenge to defend against without a strong security culture.
Common types include:
- Simple Brute Force: Tries every possible combination sequentially.
- Dictionary Attack: Uses a list of common words and passwords.
- Hybrid Attack: Combines simple and dictionary methods.
These attacks aim to:
- Take over accounts: For identity theft, fraud, or malicious activities.
- Steal data: Sensitive information like credit card numbers or personal data.
- Disrupt systems: Cause outages for financial gain or political reasons.
Brute force attacks can be time-consuming and resource-intensive for the bad actors, but they can also be highly effective, especially against weak or easily guessable passwords. The increasing affordability and accessibility of computing power make brute force attacks more common. To protect accounts and systems, individuals and organizations must adopt strong security measures to find and fix weak points in data security.
Credential Stuffing vs. Brute Force Attacks: Key Differences
While credential stuffing and brute force attacks aim to compromise user accounts, they employ distinct methodologies and pose unique challenges. However, critical differences exist in how attackers execute these attacks. Understanding these distinct attack methodologies is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies tailored to each threat.
Credential Stuffing
- Methodology: Utilizes lists of stolen or leaked credentials from data breaches, phishing scams, or website impersonation attacks.
- Target: Focuses on multiple online services simultaneously, attempting to exploit password reuse across platforms.
- Automation: Heavily relies on tools like botnets and scripts to test credentials rapidly.
- Success Rate: Often yields a higher success rate than brute force attacks due to using valid credentials.
- Consequences: can lead to account takeover, identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational damage.
Brute Force Attacks
- Methodology: Employs a trial-and-error approach to guessing passwords or PINs by systematically trying all possible combinations. It is a type of credential stuffing in which the attacker generates potential credentials rather than using stolen ones.
- Automation: This can be automated but often involves manual effort, especially for complex passwords.
- Success Rate: It generally has a lower success rate than credential stuffing attacks that utilize known credentials, especially against strong and unique passwords.
- Consequences: This can result in account takeover, unauthorized access to sensitive data, and system disruption.
While credential stuffing exploits the human tendency to reuse passwords, brute force attacks rely on computational power and persistence to crack credentials through exhaustive guessing. Both pose significant threats to online security.
8 Ways to Combat Credential Stuffing and Brute Force Attacks
Protecting your digital assets from the relentless onslaught of credential stuffing and brute force attacks demands a multi-faceted approach. While strong passwords are a fundamental first step, the sophistication of modern attacks necessitates a more comprehensive strategy.
1. Leverage Real-time Threat Intelligence
Staying one step ahead of attackers requires real-time threat intelligence that goes beyond traditional feeds and blacklists. By actively monitoring for suspicious login activity, such as failed logins from unusual locations or multiple attempts in a short period, you can detect and respond to threats as they happen.
Advanced solutions, like those offered by Memcyco, leverage behavioral biometrics and machine learning to identify credential stuffing and brute force attempts in real-time. This protects customer accounts before they’re compromised and reduces incident handling costs.
2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Adding an extra layer of security with MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if credentials are compromised. By requiring a second factor, such as a code from a mobile app or a fingerprint, you create a barrier that most automated attacks cannot overcome.
While SMS-based MFA is a standard option it has its risks – while app-based or hardware token solutions offer enhanced security due to their resistance to SIM-swapping attacks. Prioritize enabling MFA for critical accounts like email, banking, and social media.
3. Monitor Login Attempts and Detect Anomalies
Continuous monitoring of login attempts is crucial for identifying suspicious activity. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) tools can help detect anomalies. These systems can trigger alerts, enabling you to respond quickly and investigate potential threats before they escalate.
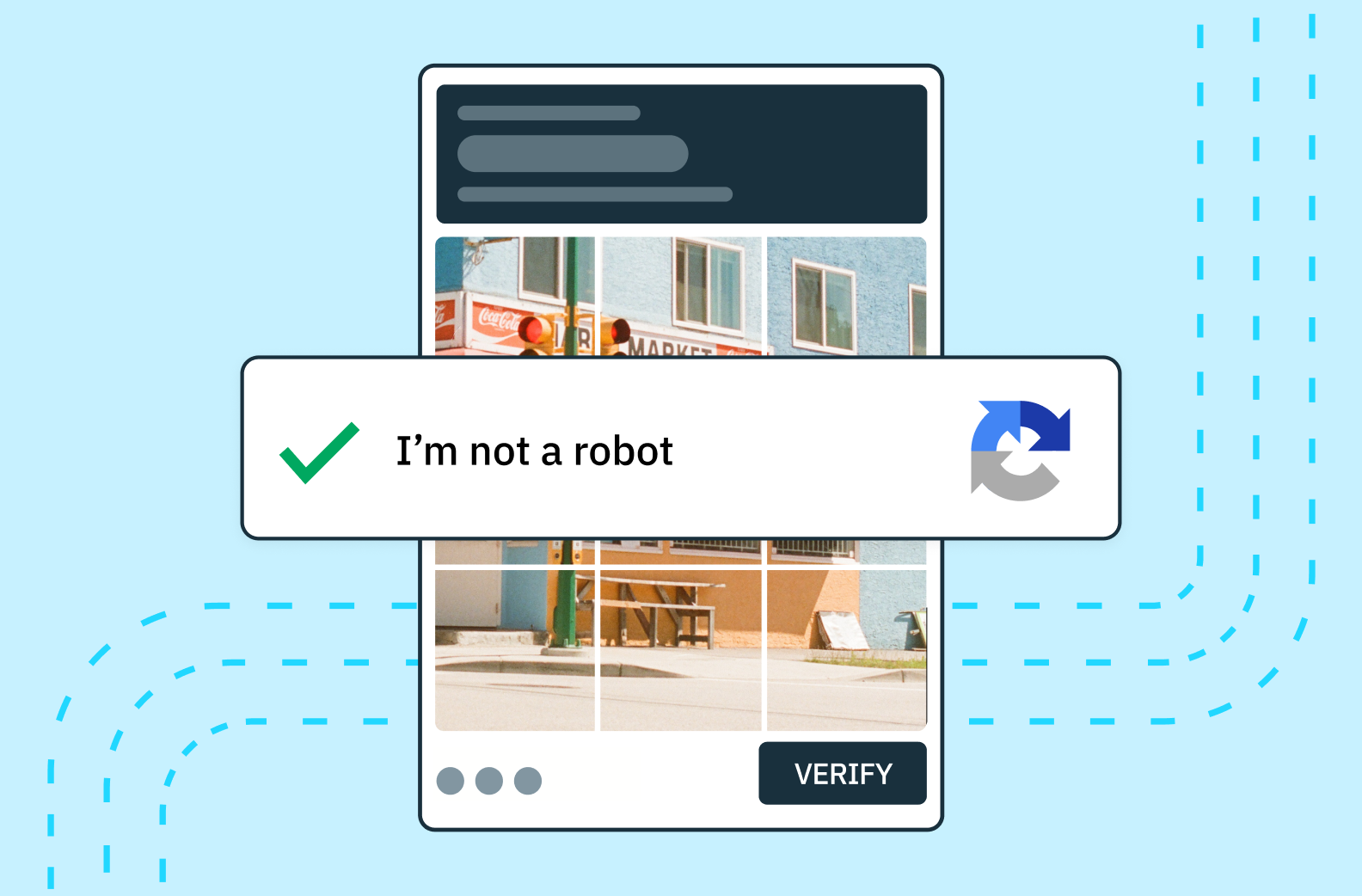
4. Use Rate Limiting and CAPTCHAs
Use Rate Limiting. Rate limiting restricts the number of login attempts from a single IP address within a specific time frame. This makes it more difficult for attackers to use brute force methods to guess passwords, as they are limited in the number of attempts they can make.
Rate limiting can be a double-edged sword. While it effectively thwarts automated attacks, it can sometimes inconvenience legitimate users who may have forgotten their passwords or are experiencing technical difficulties.
On the other hand, CAPTCHAs (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) are designed to differentiate between humans and bots. They present challenges that are easy for humans to solve but difficult for automated programs. By requiring users to solve a CAPTCHA before logging in, you add an extra layer of protection against credential stuffing attacks. However, it’s important to note that some sophisticated bots can bypass CAPTCHAs, so this method should not be relied upon as the sole defense. Also, CAPTCHAs cause customer friction which is never a good thing.
5. Implement Strong Password Policies
Encourage users to create unique, complex passwords for each account, avoiding easily guessable combinations like “123456” or personal information. Password managers can be valuable for generating and securely storing complex passwords. However, given the prevalence of password reuse and sophisticated phishing attacks, it’s crucial to recognize that strong passwords alone cannot guarantee security.
6. Implement Account Lockout Policies
Account lockout policies automatically deactivate accounts after a certain number of failed login attempts, deterring brute force attacks. While this can inconvenience legitimate users who forget their passwords, it’s a necessary trade-off for enhanced security. Consider implementing a temporary lockout period with options for password recovery to balance security and user experience.
7. Educate Users and Raise Awareness
Empowering users with knowledge about credential stuffing and phishing scams is crucial. However, even the most digitally aware individuals can fall victim to increasingly sophisticated social engineering tactics. While security awareness training is essential, it’s not a foolproof solution.
To truly protect digital trust, businesses need to go beyond education. Proactive customer protection measures that safeguard even the most vulnerable users are essential. This means implementing robust security solutions that detect and mitigate threats before they cause harm, regardless of individual user actions.
8. Adopt Software Solutions That Combat Credential Stuffing and Brute Force Attacks
While the measures above offer robust protection, the dynamic nature of cyber threats necessitates a proactive and adaptive defense strategy. Adopting specialized software solutions designed to combat credential stuffing can significantly enhance your security posture. These solutions often employ advanced technologies like machine learning and behavioral analytics to detect and thwart attacks in real-time.
For instance, Memcyco’s platform offers a comprehensive suite of tools to protect against account takeover scams, including credential stuffing and brute force attacks. By analyzing user behavior, device fingerprints, and network traffic patterns, Memcyco can identify suspicious login attempts and take immediate action to prevent unauthorized access.

The Future of Account Security is Proactive and Adaptive
The future of account security lies in proactive and adaptive solutions that can detect and respond to threats in real-time. While the old security playbook still has its uses, the bad guys are getting smarter every day, and we need to step up our game to keep up.
By leveraging advanced technologies like machine learning and behavioral analytics, Memcyco can identify and thwart credential stuffing and brute force attacks before they cause harm. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, embracing these innovative solutions will be crucial for staying one step ahead of attackers and ensuring the security of your digital assets.
Don’t wait until it’s too late. Book a demo today to see how Memcyco can safeguard your digital assets and stay ahead of the curve in account security.