Throughout history, technology has been a catalyst for solving many civilizational problems. The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) presents an incredible opportunity to combat cybersecurity risks and bolster the defenses of organizational IT networks. The good news is that it’s already making an impact by reducing the average dwell time of cyber attacks by as much as 15%. But AI holds much more promise.
However, it’s clear that, given the evolving nature of this technology and its potential misuse by cybercriminals, security teams must act quickly. CISOs should constantly keep abreast of developments in AI, and in particular in how AI is being used in the cybersecurity realm.
The Triple Dilemma of Cybersecurity
The sheer scale and speed of modern cyberattacks creates a triple dilemma that poses complex challenges to effective defense.
The Defender’s Dilemma
Defenders must protect everything, while attackers only need to find one weakness to succeed. This perpetual disadvantage puts an immense burden on security teams.
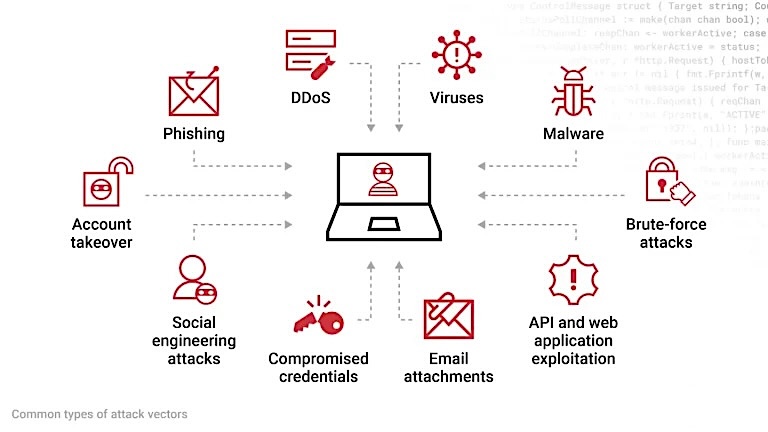
The Scale Dilemma
The “network effect” means that the more users a company has, the more valuable it becomes. However, this also creates a larger target for attackers, who can exploit this vast network to reach countless users and devices. The expanding attack surface becomes increasingly challenging to secure.
The Speed Dilemma
The Internet’s speed enables attacks to spread rapidly, outpacing the ability of humans to react and respond effectively. This velocity creates a window of opportunity for attackers to inflict significant damage before defenses can be mobilized.
These three dilemmas, taken together, make cybersecurity a constant arms race, with defenders struggling to keep pace with the evolving tactics and techniques of attackers. The need for innovative solutions to address these interconnected issues has never been greater — and that’s where AI comes in.
Rethinking the Security Architecture with AI
Traditionally, organizations have relied on various security tools, including firewalls, access control systems, antivirus, and email filters, to safeguard their IT infrastructure. However, such an architecture is built around a multi-layered configuration that is loosely defined and relatively static. This arrangement fails to adapt to the dynamics of the evolving threat landscape.
Security posture is a better way of envisaging the security architecture. It encompasses the overall security status of the organization’s IT infrastructure in objective measures and checks and balances that represent a comprehensive cybersecurity shield around the entire organizational attack surface.
With AI, an organization’s security posture can be rearranged dynamically into logical groups of scattered IT assets, allowing custom strategies to be applied based on the evolving threat perception of a group of assets. The best approach to superimpose AI on the security posture concept would be partitioning it into three independent subpostures and a fourth overall orchestrating posture.
1. External Security Posture – The AI Shield Against Outside Attacks
The external security posture establishes an ironclad shield to safeguard an organization’s public-facing IT systems, such as websites and email servers, which are constantly under attack from Internet-based attacks like phishing and website spoofing.
AI’s ability to classify massive datasets of text and media, and its predictive analytics capabilities, both help thwart such attacks. As an example, with intelligent classification AI augments the spam filtering capabilities of email and messaging applications and helps unearth hidden links contained in QR codes and PDF files, among other phenomena.
Similarly, predictive analytics can help gauge impending attacks based on historical traffic patterns – for example with DDoS attacks. At a more advanced level, it can predict zero-day vulnerabilities based on heuristic analyses of system logs and output data to detect anomalous patterns that deviate from normal system behavior.
Beyond analyzing user messages and data traffic, AI also empowers security teams to run automated real-time scans on the vast expanse of the Internet to identify fake websites impersonating the organization’s website or other public-facing IT assets. Alternatively, Memcyco is the only solution solving this exact problem in real-time, with no need for scanning, through its AI-infused external digital risk protection solution that safeguards companies and their customers against digital impersonation.
2. Interior Security Posture – An AI Guardian Protecting the IT Supply Chain
The interior security posture manages the risks associated with installing, provisioning, and upgrading the IT network and ancillary systems. It is also impacted by open-source or third-party software programs installed on the IT systems.
With at least one of every eight software packages having an inherent security risk, this subposture assumes unknown risks due to the hardware and software supplied by vendors outside the organization’s direct control.
AI-led strategies can guard against these risks in a few ways. For example, AI can scan software source code and executables for potential security loopholes or malicious code signatures.
It can also automate routine security chores such as audits and security posture scoring, which otherwise require a lot of number crunching and human effort. Automated audits of IT assets and their access permissions help predict potential threats during network and software updates.
Similarly, an amalgamation of security posture reports from vendors, cloud services, and third-party software applications helps arrive at the overall security risk score to preempt supply chain attacks.
AI also helps maintain zero trust architecture, which follows the “never trust, always verify” principle, by implementing behavioral baselining for authorized devices through device fingerprinting to proactively identify unknown or shadow IT devices. Memcyco, for example, uses a proprietary, AI-based device fingerprinting method to differentiate between legit devices and suspicious ones trying to access its customers’ websites.
3. Internal Security Posture – The AI Hawk-Eye Monitoring Insider Threats
This posture deals with the internal attack surface of the IT infrastructure that is under threat from employees, contractors, and other users within the organization.
The internal posture is reinforced through identity and access management (IAM) systems that manage user identities, authentication, and authorization procedures. With AI, this mechanism is further strengthened through periodic reviews of access rules and permissions of all IT assets to ensure adherence to the principles of least privileges and detection of access blind spots.
AI’s predictive analysis and adaptive learning capabilities also help fortify this posture. Predictive behavioral analytics identifies the Indicators of Compromise (IoC) among users, such as increased system activity from privileged user accounts, frequent file downloads, or database record access.
Adaptive learning enforces risk-based authentication based on location, timings, and other parameters within the historical login data to dynamically change authentication factors.
4. Unified Security Posture – The Generative AI Maestro Orchestrating It All
All organizations leverage Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and other detection and response systems that significantly contribute to determining the company’s security postures. Therefore, it’s also crucial to consider the role of AI in consolidating all cybersecurity-related workflows for easier management.
Generative AI plays a significant role here. It automates the creation of incident response reports based on known threat patterns, self-assessment of incident severity and classification, and guided response playbooks to work through the incident workflow.
Additionally, it also aids in building a threat model for attack simulation based on system logs and public threat intelligence data. These models are beneficial for performing periodic penetration testing through AI agents to verify the resilience of the overall security posture.
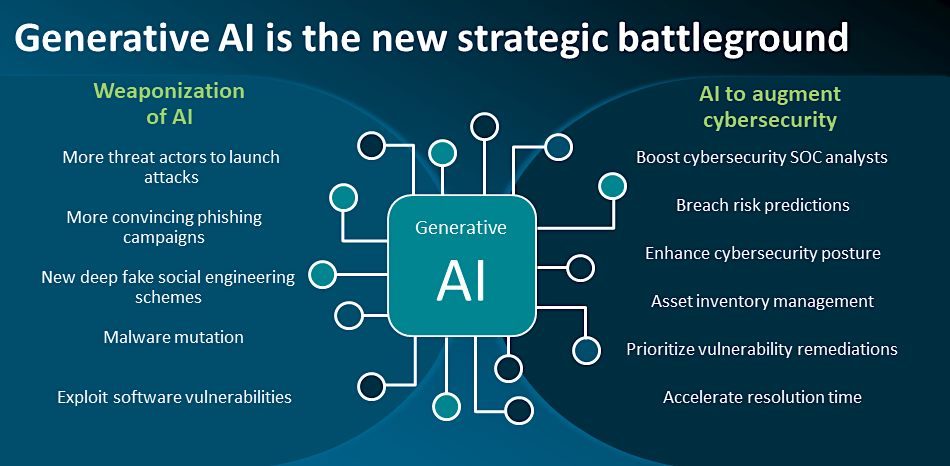
AI Improving Cybersecurity: Balancing Innovation with Vigilance
Today’s enterprise cyber landscape faces a stark reality: “There are two types of companies: those who have been cyber-attacked, and those who haven’t, yet.” So, the question isn’t if an attack will occur—but when.
AI plays a transformative role in this relentless battle. A modular approach based on these four security postures enables the progressive integration of AI into a company’s cybersecurity strategy. Doing so can effectively reduce the defender’s dilemma, enabling a proactive and adaptive approach to safeguard organizational IT and digital assets while offering unparalleled capabilities in mitigating the scale and speed of cyber attacks.
Employing innovative solutions like Memcyco’s AI-powered, real-time digital impersonation protection helps organizations stay ahead of fraudsters and protect their digital assets with brand impersonation monitoring and alerting. In action, it’s a prime example of the best-case scenario for how AI is improving cybersecurity now and how other solutions might follow in the future.