As tech stacks modernize, traditional security solutions quickly become outdated.. In 2024, 94% of companies are using cloud computing services to some extent. As more companies step away from legacy infrastructure, taking a proactive approach to cloud network security becomes a priority.
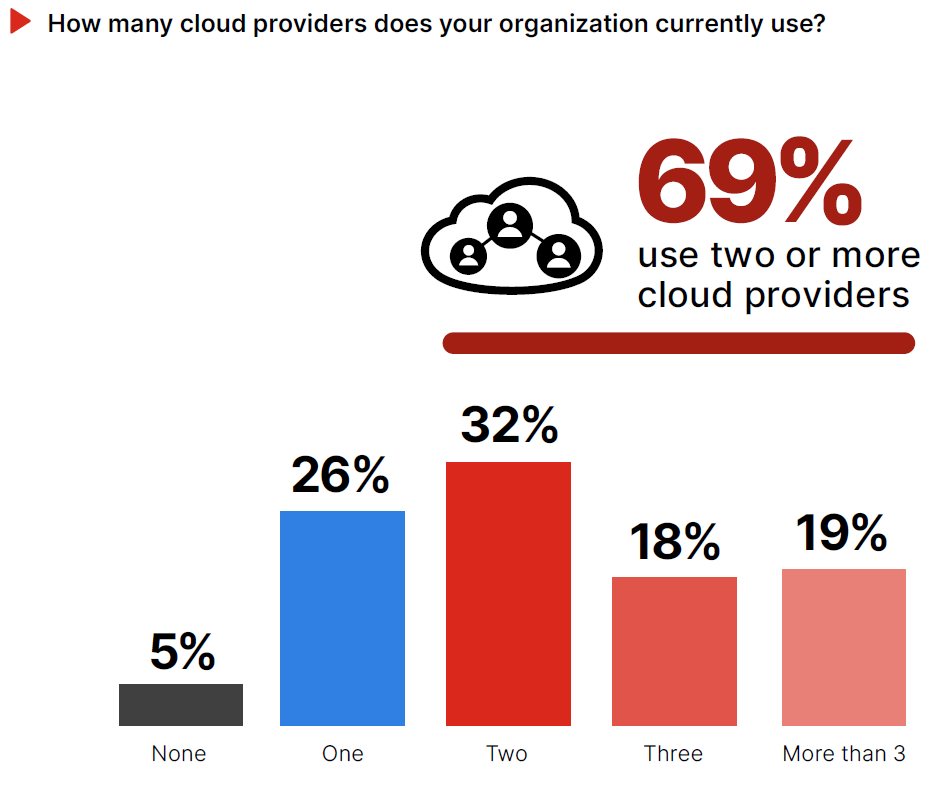
It’s easy to picture “the cloud” as a single mass entity, but enterprises use an average of 1,295 different cloud services, often from multiple vendors. And it’s not just enterprise companies that are migrating to the cloud in high numbers: 63% of small and medium businesses (SMBs) workloads are now hosted in the cloud, and the majority use more than one cloud provider.
It’s important to acknowledge that these services bring innovation opportunities, but they also bring challenges. For example, not accounting for the multiple elements that make up these expanding attack surfaces leaves your company at risk. With most organizations of all sizes adopting multi- or hybrid-cloud, it becomes increasingly complex to maintain and manage security for their multiple environments.
Migrating data from on-premises data centres to the cloud can raise various security risks. This doesn’t go unnoticed by malicious hackers who look for opportunities to steal personal information or plant malware to gain access to corporate networks when data is in its most vulnerable state.
Research has found that once a system has been breached, the average amount of time these attackers can operate undetected is 8 days. Irreparable damage can be done in that time.
If you’re among the 94% of businesses considering cloud network security their top priority, here are some issues to look out for and best practices to prevent them.
Understanding Network Cloud Security
Cloud network security aims to limit the opportunities malicious actors may find to access, change, or destroy information on private or public cloud networks.
Due to the unique qualities of cloud environments, different approaches and tactics are required compared to on-site networks. As organizations of all sizes migrate to the cloud, more sensitive information than ever is being stored on cloud networks, attracting all kinds of malicious actors.
3 Cloud Security Challenges
While the cloud offers numerous benefits, it also comes with several security challenges that businesses should be aware of. These include:
1. Compliance Requirements and Contractual Breaches
With regulatory control increasing, there is a growing range of strict compliance requirements surrounding how your company handles its data, who has access to it, how it is processed, and how it is protected.
You may also have contractual partnerships stipulating how shared data is stored, used, and accessed. Being unaware of these regulations could lead to careless data transfers and put your organization at risk of non-compliance or breach of contract, potentially exposing you to hefty legal and financial repercussions.
2. Insider Threats
The biggest security risks are often your employees, contractors, and business partners. This isn’t necessarily due to malicious intent but commonly happens due to negligence, naivety, distraction, and lack of training. Arguably, when you migrate data to the cloud, you add another layer to this threat by handing over sensitive information to the cloud provider’s employees.
3. Misconfiguration of Cloud Services
As cloud services grow increasingly complex with a wider range of features, misconfiguration of cloud services can be a security risk. Given how many organizations use multiple cloud providers, preventing security vulnerabilities becomes increasingly complex. Cloud misconfiguration can allow for sensitive data to be publicly exposed, changed, or deleted and can commonly be caused by leaving default settings in place.
The Shared Responsibility Model
The shared responsibility model is used to clarify who is responsible for which parts of your data security. By shifting your data to the cloud, you’re opting to share the responsibility for securing that data with a cloud service provider. An unambiguous shared responsibility model ensures there is no gap in your security coverage.
The responsibilities that fall to each party will vary depending on the type of service and the service provider you choose. But generally speaking, the shared responsibility model can help protect you and your company from the reputational, financial, and legal ramifications that follow data loss and data breaches.
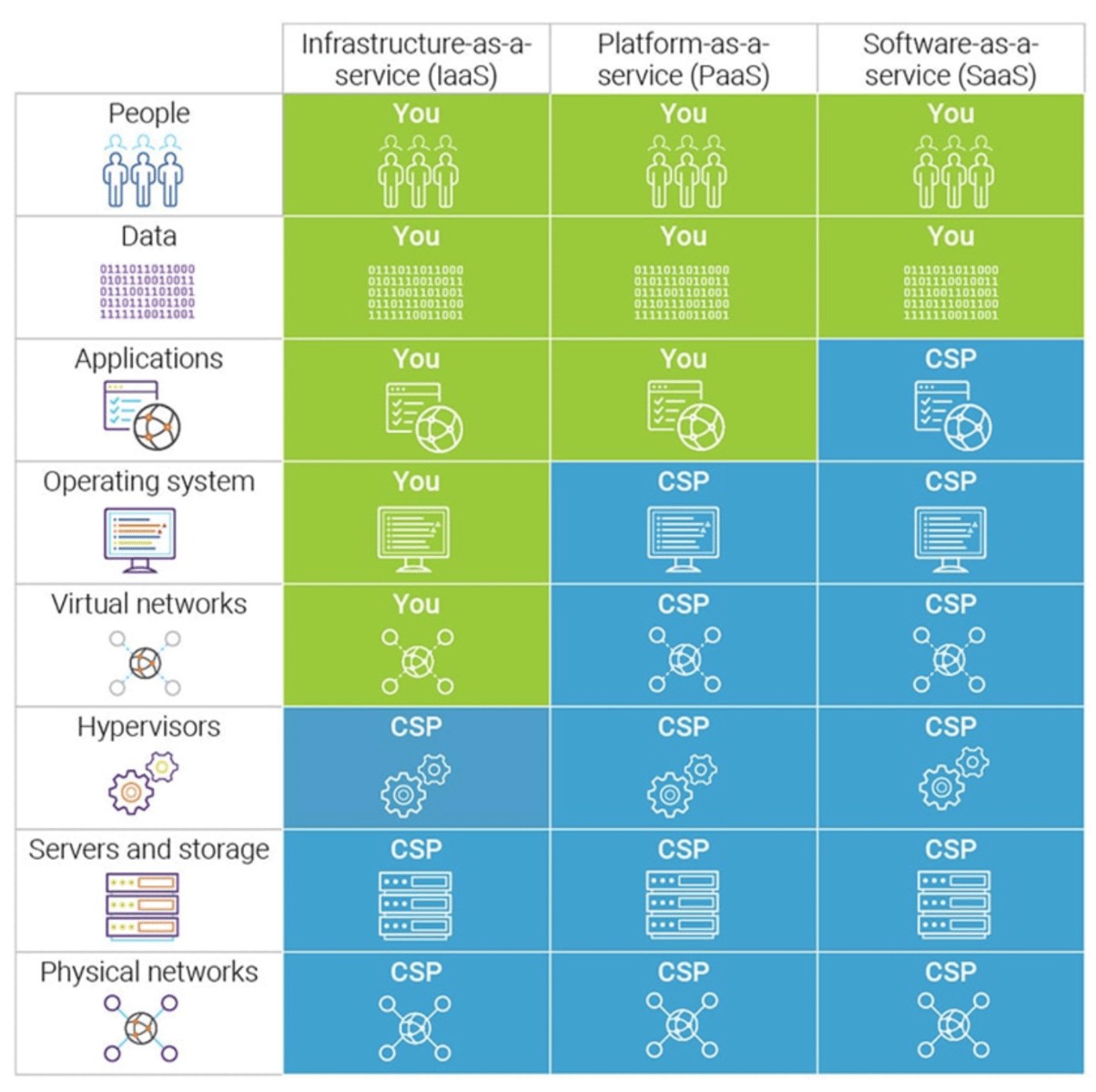
Figure 4. Shared Responsibility Model. From “A Comprehensive Guide to Cloud Security in 2022 (Risks, Best Practices, Certifications,” by E. Jones, 2022, September 30.
6 Essential Steps To Improve Your Cloud Network Security
1. Implement IAM
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a cloud service that determines the permissions and user access to cloud resources. It is a set of permissions policies that determines who can access what information in the cloud resources and what users can do with that information. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an example of IAM that is easy to implement and has been shown to protect up to 99% of fraudulent sign-in attempts.
2. Encrypt Your Data
Encrypting the data you transfer to the cloud ensures it is concealed from unauthorized or malicious users. This service is automatically included in the offerings of some cloud providers that deliver end-to-end protection of data being transferred to and from the cloud, as well as resting data stored in the cloud, preventing it from being manipulated.
3. Protect User Endpoints
Endpoint devices are laptops, desktop computers, servers, mobile devices, or any other type of technology that can connect to a network and can, therefore, be used as access points by hackers. As the use of unmanaged devices connecting to cloud traffic has doubled due to remote working and IoT trends, it is critical to educate employees about the importance of accessing the cloud network exclusively from a protected endpoint device. With proper endpoint protection, malware and other threats to the network can be found and resolved quickly.
4. Maintain Logs and Monitoring
Maintaining logs and monitoring systems can help organizations detect unauthorized activities. This allows security teams to identify a user making any damaging changes to the network and resolve the issue quickly. By setting up alerts to inform you of any unusual events, you can save your company valuable time and money.
5. Employ a Robust Security Strategy with Strong Authentication
While a strong password strategy remains important, modern security practices go beyond passwords alone. Consider these elements:
- Passwordless Authentication: Prioritize passwordless authentication methods like biometrics (fingerprint, facial recognition), hardware tokens, or one-time codes sent to mobile devices. This eliminates the risk of weak or reused passwords.
- Strong Passwords (If Used): Where passwords are still necessary:
- Length: 12 or more characters (not just 8).
- Complexity: Mix uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Uniqueness: Avoid reusing passwords across different services.
- Regular Changes: Change passwords periodically, even if no compromise is suspected.
- Password Managers: Encourage the use of password managers to generate and securely store complex passwords. This reduces the burden on users remembering multiple credentials.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA wherever possible. This adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide another factor (e.g., fingerprint, code) in addition to their password.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate employees about the importance of strong authentication practices, the risks of phishing and social engineering attacks, and how to identify suspicious activity.
6. Perform Pen Testing to Find Gaps
Penetrating testing (a.k.a. pen testing) is a type of security test intended to find a system’s vulnerabilities by forcing access onto it. It can be used to find weaknesses both in on-site systems and cloud networks. Pen tests are efficient in finding vulnerabilities because pen testers use the same tools, techniques, and processes as attackers to find and demonstrate the business impacts of weaknesses in a system, alerting security teams to how attackers may exploit them.
Moving Forward With Confidence and Trust
As more businesses migrate to cloud networks, it’s important to follow best practices when it comes to your cloud network security. There is a lot of responsibility that comes with private information and sensitive data that requires protection. Failing to adequately protect this data could leave your company dealing with huge financial losses, legal consequences, and even possible shutdowns. By choosing the right cloud service provider, you have someone to share that responsibility with so that you can focus on growing your business instead of managing infrastructure with security and damage control. Learn more about how Memcyco can support your security efforts.